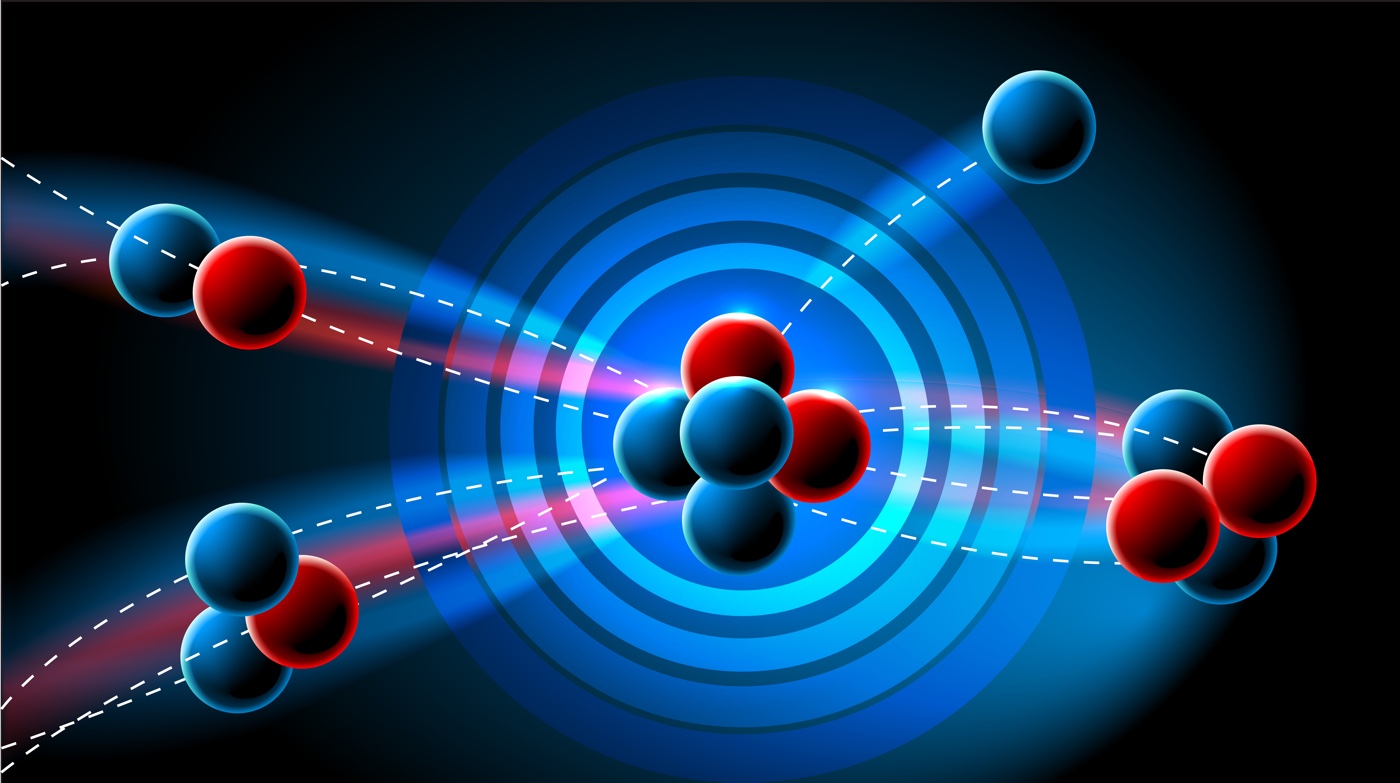
Nuclear reactions are collisions between two atomic nuclei or one atomic nucleus and a subatomic particle that produce one or more nuclides. Nuclear reactions yield nuclides that are distinct from the parent nuclei.
Nuclear fusion and nuclear fission are two well-known forms of nuclear processes. Nuclear fusion reactions are collisions between two relatively light nuclei that result in forming a single, heavier nucleus. Nuclear fission occurs when a heavy nucleus absorbs neutrons or other comparatively light particles, causing it to divide into two lighter nuclei.
The Energy Released during a Nuclear Reaction
The atomic nucleus’ mass is always smaller than the sum of the masses of each subatomic particle that makes it up. Nuclear binding energy is responsible for the mass difference. Nuclear binding energy is the energy necessary to keep all of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus together.
The mass accounted by the nuclear binding energy is released during a nuclear reaction (fission or fusion process). According to the equation,
E(energy) = mc2
- m – mass
- c – speed of light
Nuclear fission and nuclear fusion products are always lighter than reactants to make things easier.
Nuclear Fusion
Nuclear fusion occurs when the nuclei of two light atoms fuse to generate a new nucleus. In a fusion reaction, the combined mass of two light nuclei is smaller than the combined mass of the two individual nuclei. The reaction of Deuterium and Tritium, both isotopes of hydrogen, to produce Helium, which releases a neutron and releases roughly 17 MeV of energy, is an example of fusion.
Benefits of Nuclear Fusion
The following are some of the benefits of nuclear fusion:
- It is a reliable source of electricity generation.
- The amount of fuel accessible in nature is cheap and abundant.
- The amount of greenhouse gases released during the fusion process is negligible.
Nuclear Fission
Breaking a heavy nucleus, including uranium or plutonium, into two smaller nuclei of nearly equal mass is known as nuclear fission. The unstable radioactive nucleus is split into two smaller nuclei during this procedure. Nuclear fission can happen naturally in some instances or be caused by bombarding the nucleus with particles or gamma-ray radiation.
- During the fission reaction, a tremendous quantity of energy is released, resulting in radioactive materials and the discharge of many neutrons.
- These neutrons can cause a chain fission process in the uranium or plutonium nucleus, releasing further neutrons.
- It can lead to an uncontrollable chain reaction that continues until all of the initial material has been used up, releasing a tremendous quantity of energy in the process.
Advantages of Nuclear Fission
The advantages of nuclear fission are:
- It is a clean alternative energy source that meets the demands of both current and future generations.
- Global warming and greenhouse gas production are less of a threat.
- Operational costs are incredibly minimal.
Limitations of Nuclear Fission
Humans and animals are susceptible to the radiation emitted during the fission reaction. Humans who are directly exposed while operating at nuclear power plants are at a high risk of developing cancer, radiation sickness and other radiation-related illnesses. The disadvantages of nuclear fission are:
- Radiation exposure is more dangerous.
- Extremely vulnerable
- Risk of radioactive contamination
- Plant commissioning is expensive.